unrealistic optimism definition|optimist vs realist : Clark We summarize the vast literature on unrealistic optimism by focusing on four . Most twin pairs eventually find ways to repair their relationships and mitigate their rivalry as they find and define their individual life paths and identities. If you have a story about a twin .
unrealistic optimism definition,In order to assess such claims, we need to explain what unrealistic optimism is, whether the cognitive states that are unrealistically optimistic are belief states, and to what extent they are false. If such cognitive states can be said to be false or epistemically irrational .How unrealistic optimism is maintained in the face of reality. Nat Neurosci. 2011; .We summarize the vast literature on unrealistic optimism by focusing on four .Abstract. Here we consider the nature of unrealistic optimism and other related .Unrealistic optimism is a pervasive human trait influencing domains ranging from .
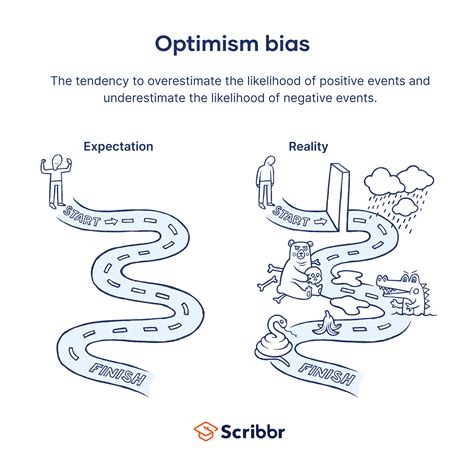
In the case of absolute unrealistic optimism, a prediction is unrealistically positive compared to the objective likelihood of an event occurring. In contrast, in . Here we consider the nature of unrealistic optimism and other related positive illusions. We are interested in whether cognitive states that are unrealistically . Because unrealistic optimism is, by definition, an expectation that is more favorable than what likely will occur, people who display unrealistic optimism will .unrealistic optimism definition People display unrealistic optimism in their predictions about countless events, believing that their personal future outcomes will be more desirable than can .
People display unrealistic optimism in their predictions about countless events, believing that their personal future outcomes will be more desirable than can . TLDR. Drawing from 3 decades of research, critically how researchers define unrealistic optimism is discussed, and four types of unrealistic optimism are . Unrealistic optimism—expecting future outcomes that are better than is reasonably likely—has received enormous attention over the last four decades, with over 1000 articles published on the topic since the first publication on the topic by Weinstein (1980). . We define saving regret as the wish in hindsight to have saved more earlier in .We define unrealistic optimism as a favorable difference between the risk estimate a person makes for him- or herself and the risk estimate suggested by a relevant, objective standard (such as epidemiological, base-rate data). Unrealistic optimism also includes comparing oneself to others in an unduly favorable manner. Our definition makes no .unrealistic. (ʌnriəlɪstɪk ) adjective. If you say that someone is being unrealistic, you mean that they do not recognize the truth about a situation, especially about the difficulties involved in something they want to achieve. [.] unrealistically (ʌnriəlɪstɪkli ) adverb [ADVERB with verb, ADVERB adjective]

1. Introduction. Unrealistic optimism—expecting future outcomes that are better than is reasonably likely—has received enormous attention over the last four decades, with over 1000 articles published on the topic since the first publication on the topic by Weinstein (1980).Research on unrealistic optimism appears in a variety of .

Unrealistic optimism about risk is often viewed as but one aspect of a more general self-enhancement bias that also encom-passes phenomena such as the planning fallacy (e.g., Buehler & . refer to a mean, median, or mode. In terms of detecting unreal-ism, simple majorities are useless, as it is readily possible to be .optimist vs realistUnrealistic optimism about risk is often viewed as but one aspect of a more general self-enhancement bias that also encom-passes phenomena such as the planning fallacy (e.g., Buehler & . refer to a mean, median, or mode. In terms of detecting unreal-ism, simple majorities are useless, as it is readily possible to be .
Unrealistic optimism is positively related to dispositional optimism but often shows different relationships to outcomes. There is also research on defensive pessimism, strategic optimism, hopeless pessimism, and situated (or situation-specific) optimism, as well as related concepts such as hope and illusion of control. .
Realistic optimists believe that they can succeed, which encourages them to try, but they also know that persistent effort is the only way to succeed, so they work very hard. Unrealistic optimism – the stuff of vision boards and the so-called “law of attraction” – discourages hard work.Unrealistic optimism is a pervasive human trait influencing domains ranging from personal relationships to politics and finance. . Participants were generally optimistic; the mean optimism score was 15.68 (range 7–21, SD = 3.98). We divided participants into those that scored higher than the mean (“high optimism” group n = 11, mean = 18 .Researchers have used terms such as unrealistic optimism and optimistic bias to refer to concepts that are similar but not synonymous. Drawing from three decades of research, we critically discuss how researchers define unrealistic optimism and we identify four types that reflect different measurement approaches: unrealistic absolute optimism at the .The first type is unrealistic absolute optimism , optimistic propensity appears for desirable events, such which refers to an unjustified belief that a personal out- as graduating from college, getting married, and having come will be more favorable than the outcomes indi-. favorable medical outcomes (e.g., Weinstein, 1980).
Unrealistic optimism is all around us, and it is a well-documented psychological phenomenon. The purpose of this study is to take a critical approach of the main research done in the area and to analyze the important impact that it has in many economic and managerial contexts. We also analyze current trends in terms of . Unrealistic optimism allows us to have a rosier view of our own future than is justified by the evidence available to us, but this outlook is constrained by external pressures which push us towards a more .
unrealistic optimism and absolute realism or comparative realism and absolute unrealistic optimism. Depending on the case and the kind of unrealistic optimism exhibited, people are mistaken about .unrealistic optimism definition optimist vs realistAbstract. Here we consider the nature of unrealistic optimism and other related positive illusions. We are interested in whether cognitive states that are unrealistically optimistic are belief states, whether they are false, and whether they are epistemically irrational. We also ask to what extent unrealistically optimistic cognitive states are . UNREALISTIC OPTIMISM definition | Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples
Shepperd J. A., Klein W. M. P., Waters E. A., Weinstein N. D. (2013). Taking stock of unrealistic optimism. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8, 395–411. Provides a detailed review of three decades of research on unrealistic optimism and responds to recent methodological criticisms of the field. Unrealistic optimism or optimism bias—the tendency for individuals to overestimate the chance of favorable outcomes occurring and underestimate the chance of bad (Weinstein, 1980)—has been found to be one of the most pervasive human traits across many domains (Sharot, 2011).For instance, research has shown that individuals .
Unrealistic optimism is defined as the “tendency for people to believe that they are less likely to experience negative events and more likely to experience positive events than are other people” . This definition agrees with the claim of stress theories that the major function of coping is to reduce fear and anxiety, .
unrealistic optimism definition|optimist vs realist
PH0 · optimistic realist definition
PH1 · optimist vs realist
PH2 · Iba pa